Stainless steel represents a material that possesses both long-lasting strength and adaptable functions, and a contemporary architectural style. 304 stainless steel sheets exist as the most common industrial material that people select for use in both construction projects and food processing facilities. The specific qualities of this grade create its worth, which enables its use in different fields. The article investigates 304 stainless steel sheets through their unique qualities, which include their physical characteristics, industrial advantages, and their essential functions across multiple sectors. The article provides essential knowledge that exists to help manufacturers, architects, and people who wish to understand how stainless steel shapes their environment.
Introduction to Stainless Steel Sheet Metal

What is Stainless Steel Sheet Metal?
The unique properties and practical benefits of stainless steel sheet metal create an industrial-grade material that functions across multiple applications. The alloy contains primary components of iron and chromium, but also includes nickel to create a material that resists both oxidation and staining in environments with high moisture and extreme pressure. The exceptional welding properties of 304 stainless steel create its standing as one of the most valuable stainless steel grades because of its high strength and ability to withstand extreme heat and chemical exposure.
Manufacturers use gauge standards to measure stainless steel sheets, which they produce in different thicknesses that range from 30 gauge to 7 gauge and higher, depending on their specific application requirements. These sheets find applications in various industries, which include construction, automotive, medical, and food processing. The chemical composition of 304 stainless steel contains 18-20% chromium and 8-10.5% nickel, which provides excellent anti-corrosive protection and makes it appropriate for multiple uses, which include kitchen appliances and chemical storage tanks.
The global stainless steel sheet and strip market reached a valuation above $94 billion in 2022, according to current market research, which predicts a market growth rate of 5-6% between 2023 and 2030, driven by construction, transportation, and industrial machinery demand. This data reflects the material’s growing importance in modern manufacturing and design. Engineers rely on stainless steel sheet metal as a dependable material that they use to develop intricate architectural designs and durable industrial constructions.
Overview of 304 Stainless Steel
304 stainless steel is one of the most widely used grades of stainless steel, which provides excellent corrosion resistance and durability for various applications. The material exists as an austenitic stainless steel that contains 18 percent chromium and 8 percent nickel and small amounts of carbon and manganese. The 304 stainless steel combination produces non-magnetic materials that provide high oxidation and corrosion protection for indoor and outdoor use.
The primary property that defines 304 stainless steel is its capacity to maintain structural strength across a broad temperature range. The food and beverage industry uses this material because it maintains high hygiene standards while providing resistance to rust and chemical reactions with food products. The material finds common application in kitchenware, chemical containers, architectural panels, and automotive components.
Recent industry data highlights the growing demand for 304 stainless steel, particularly in high-performance applications. Market research indicates that the global stainless steel market value will surpass $240 billion by 2027, with 304 stainless steel expected to capture a major market share because of its affordable price and wide range of applications. The material achieves recyclability, which supports environmental sustainability, and this property drives its use in various business sectors.
The manufacturing and design fields depend on 304 stainless steel as a strong and trustworthy material that supports their innovative development.
Importance in Various Industries
The primary materials that 304 stainless steel provides to various industries maintain essential functions because its three fundamental characteristics offer both strength and oxidation protection at a low cost. The construction industry selects this material because its long-lasting nature and visual attractiveness make it suitable for use in architectural components that include cladding and handrails, and structural supports. Recent market reports show that the building and construction sector uses more than 35% of total stainless steel demand, while 304 stainless steel serves as the primary material because it maintains structural integrity under extreme environmental conditions.
The automotive industry benefits from 304 stainless steel because its exceptional heat resistance and corrosion protection make it appropriate for exhaust systems, fuel tanks, and decorative trim. Automotive manufacturers have reported a steady rise in their stainless steel usage since 2023. Existing production levels will reach above 22 million metric tons by 2025 because of electric vehicle technology advancements.
The food and beverage industry depends on 304 stainless steel for its operations. The non-reactive surface of this material enables hygienic processing and storage equipment, which includes tanks and piping, and kitchen appliances, to meet current strict safety requirements. The stainless steel market within this sector will experience annual growth of 6% because there is increasing demand for eco-friendly and hygienic products.
In healthcare, 304 stainless steel provides essential materials for surgical instruments, implants, and medical devices because of its compatibility with biological systems and simple sterilization process. The medical stainless steel market worldwide is projected to achieve a $7 billion valuation by 2026, which highlights its vital role in developing contemporary healthcare technology
Multiple industries use 304 stainless steel because its properties help them to expand their business activities while they work to protect the environment.
Types of Stainless Steel Sheets

304 Stainless Steel Sheet vs. 316 Stainless Steel
The 304 stainless steel sheets provide affordable durability and corrosion resistance, which multiple industries use to test their different operational needs. The grade combines 18-20% chromium with 8-10.5% nickel to create materials that protect against oxidation and corrosion in all environmental conditions. The metal serves multiple purposes because it possesses essential characteristics that make it appropriate for kitchen appliances, chemical containers, and architectural structures.
The 316 stainless steel sheets receive improved properties through their molybdenum content, which typically ranges between 2-3% of the total material. The metal gains enhanced protection against pitting and chloride corrosion through this element, which makes it suitable for marine applications and environments with saltwater, chemicals, and high-temperature conditions. The unique characteristics of 316 stainless steel make it the preferred material for medical devices, marine equipment, and food processing environments.
The global stainless steel market reached a value of approximately $104 billion in 2022, according to the latest industry insights, which showed that manufacturers preferred 304 and 316 grades as their primary materials. The market demand for stainless steel will experience growth at a compound annual growth rate of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030 because industrialization progresses and more people seek eco-friendly materials. The general-purpose applications of 304 stainless steel make it preferred by users, while 316 stainless steel serves better for extreme conditions because its advanced capabilities justify the higher expenses.
The technological progress and industrial innovation of various sectors depend on the essential contributions that 304 and 316 stainless steel sheets provide to their respective industries. The two grades enable industries to solve different problems because they provide solutions that match their operational needs for either price efficiency or advanced corrosion protection.
Key Differences Between 304 and 316 Stainless Steel
The industrial and commercial sectors use 304 and 316 stainless steel because these materials provide multiple functions for different purposes. The composition of 304 stainless steel contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel, which makes the material suitable for general use as an affordable option. The 316 stainless steel alloy contains 16% chromium, and 10% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum, which enhances its protection against corrosion from chlorine and seawater.
- Comparison of Corrosion Resistance
The two material grades demonstrate different responses to corrosive elements because their chemical makeups establish distinct protective mechanisms. Recent studies demonstrate that 316 stainless steel provides better resistance against saltwater and dangerous chemicals than 304. The material serves ideal functions in marine environments and chemical processing plants, and industries that face extreme weather conditions. The material displays good performance under typical conditions, but 304 stainless steel develops rust and pitting when it comes into contact with highly salty environments. - Cost and Availability
The cost of 304 stainless steel remains lower than that of 316 stainless steel because industry reports show 304 stainless steel costs 20-30% less than 316 stainless steel. The material serves as a preferred option for budget-sensitive projects because it offers both low-cost and widely available options. The superior properties of 316 stainless steel justify its elevated price because businesses need materials that can withstand demanding conditions for extended periods. - Applications by Sector
The recent research shows that 304 stainless steel serves as the primary material for kitchen equipment, automotive parts, and architectural structures that need protection from corrosion. The medical sector prefers 316 stainless steel for surgical instruments, while offshore platforms, pharmaceutical equipment, and food processing facilities use the material because of its ability to resist chemical and contamination damage.
The complete understanding of 304 and 316 stainless steel demonstrates the unique benefits that each material provides. The correct grade selection protects application lifespan while maintaining peak performance and cost-efficiency.
Applications of 430 Stainless Steel
430 stainless steel is a ferritic steel alloy that delivers both strong corrosion resistance and the ability to produce smooth surface finishes. The material serves as a cost-effective solution that functions in multiple industrial applications that require basic corrosion protection, which falls short of 304 and 316 stainless steel grade protection. The upcoming part of the document shows particular use cases that demonstrate their essential attributes.
- Kitchen Appliances and Utensils
The production process for kitchen sinks, range hoods, and cutlery requires 430 stainless steel because it provides an ideal combination of aesthetic value and durable strength at an affordable cost. The material proves suitable for visible surfaces because it maintains its shiny appearance throughout extended periods of use. - Automotive Trim and Exhaust Systems
The automotive industry frequently uses 430 stainless steel for decorative trim and certain parts of exhaust systems where high-temperature resistance is required. The material provides oxidation protection at high temperatures, which results in longer product durability. - Industrial Applications
The chemical industry uses 430 stainless steel for the construction of nitric acid plant equipment and other chemical process equipment, which demands protection against moderate corrosive conditions. The material serves as a suitable option for manufacturing solenoid and valve components because of its magnetic characteristics. - Building and Construction
This grade of stainless steel provides both visual appeal and structural strength, which makes it suitable for use in roofing and cladding systems as well as elevator panels and various decorative hardware components. - Food Processing Equipment
The production of food-contact equipment, such as trays and storage containers, requires 430 stainless steel because it meets hygiene standards in areas with limited chemical exposure.
Key Data and Properties
- The material contains approximately 16-18% chromium, which provides its capacity to resist corrosion.
- The material exhibits thermal conductivity that exceeds that of austenitic grades, thus making it appropriate for use in heat exchangers.
- The 430 stainless steel material exhibits high magnetic strength, which sets it apart from most other stainless steel grades.
- The price of 430 stainless steel is significantly lower than that of grades 304 and 316. The material costs between 20% and 30% less than other materials based on current market trends.
The use of 430 stainless steel in suitable applications operates as a budget-friendly option that delivers dependable results in settings that experience low corrosion and need decorative elements.
Properties of Stainless Steel

Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steel
The protective oxide layer on stainless steel surfaces develops because chromium content in stainless steel provides the metal with its corrosion resistance. The protective layer blocks all oxygen and moisture from entering the material, which results in protection against rust and material breakdown throughout different environmental conditions. The stainless steel grades exhibit various corrosion resistance levels because their specific environmental conditions need to test their particular material compositions.
The composition of Grade 304 stainless steel includes 18% chromium and 8% nickel, which enables the material to provide superior protection against oxidation when exposed to both atmospheric conditions and mild corrosive environments. The combination of 2-3% additional molybdenum with Grade 316 improves its resistance against pitting and crevice corrosion because the metal protects against marine environments that have high chloride content.
Research studies demonstrate that Grade 430 with its chromium content of approximately 16-18% performs well in indoor settings that experience mild corrosion and in decorative applications that do not require critical protection, but fails to protect against aggressive environments that include salty and acidic conditions. The industry reports show that Grade 316 provides 20-30% greater chloride resistance than 304, which makes it the better option for use in coastal areas and chemical processing facilities.
The selection of the right stainless steel grade needs to match the specific environmental conditions that exist at that particular location. The material requires 316 stainless steel or specialized alloys for use in environments that experience prolonged extreme weather conditions, high heat, and acidic substance exposure. The maintenance process helps to preserve the passive protective coating, which provides everlasting protection against corrosion damage.
Durability and Strength of 304 SS
With its outstanding strength and durability properties, 304 stainless steel has become the preferred material for multiple industrial applications. Recent data shows that this stainless steel grade has a tensile strength of approximately 505 MPa (73,200 psi) and a yield strength of about 215 MPa (31,200 psi). The material exhibits properties that enable its use in building construction and various industrial applications.
The material demonstrates an approximate break elongation of 70%, which proves its capacity to withstand deformation until it reaches the failure point, thus enhancing its load-bearing ability. The hardness of 304 stainless steel reaches approximately 201 HB on the Brinell scale, which provides an effective combination of material strength and capacity to be shaped.
Recent findings demonstrate that 304 maintains its strength and deformation resistance from temperatures of -200°C to 870°C (-328°F to 1600°F). The higher temperature and aggressive chemical exposure environment requires users to choose 316 stainless steel as their better option.
Engineers choose 304 stainless steel for their projects because its buildable data points provide cost-effective flexibility and strong durability.
Impact of Thickness on Performance
The mechanical properties, thermal conductivity, and total performance of 304 stainless steel depend on its thickness. The flexibility and shapeability of 304 stainless steel become better with thinner sheets, which makes them suitable for use in automotive panels and architectural finishes. Thinner materials will exhibit decreased mechanical strength because they lack the capacity to withstand both heavy loads and impact forces.
The material properties of 304 stainless steel improve when its sections become thicker because this change increases durability and load-bearing capacity and decreases deformation under stress. A 5mm thick 304 SS sheet can resist up to 210 MPa (megapascals) tensile stress according to recent data, which matches its maximum tensile strength specification of approximately 505 MPa.
Thicker materials display lower thermal efficiency for heat conductivity because their longer heat transfer distances reduce thermal performance. The thermal expansion coefficient of 304 stainless steel remains constant at 17.2 µm/m°C, which allows the material to function effectively across different temperature ranges.
The optimal thickness of 304 stainless steel needs to be established through evaluation of specific mechanical requirements, environmental factors, and intended usage. The analysis of these parameters enables projects to achieve benefits from both material characteristics and practical adaptability.
Fabrication Techniques for Stainless Sheet Metal
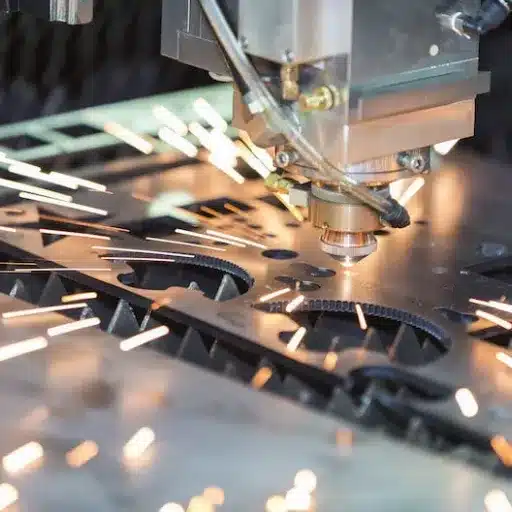

Common Fabrication Methods
The sheet metal of 304 stainless steel serves multiple design purposes because it can be processed using different manufacturing techniques. The following list presents the most widely used manufacturing techniques in industrial production:
1. Cutting
The stainless steel sheets undergo cutting operations through three techniques, which include laser cutting, plasma cutting, and shear cutting. The laser cutting technology focuses on achieving high precision, which permits tolerances up to 0.005 inches for material cutting. The method operates by using high-powered lasers to cut sheet materials that have thicknesses between 0.02 inches and 1.25 inches. The modern laser cutters possess advanced capabilities that enable them to produce clean edges that do not have burrs and can handle intricate design tasks.
Plasma cutting operates by using electrically conductive gas to perform cuts on materials that have thicknesses reaching 2 inches. The method achieves less precision than laser cutting but remains effective for building strong structures. Shearing provides a quick and economical solution that enables operators to perform straight cuts on sheets that have thicknesses below 0.25 inches.
2. Bending
The bending process of stainless steel sheets requires two different machines, which include press brakes and roll bending machines. The press brake systems utilize CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology to generate precise angle measurements, which enable bending operations to achieve tolerances between ±0.2° and ±0.5°. The process creates structural elements that include brackets and frames. Welders must consider spring-back effects, which occur during the bending process, because of stainless steel’s high tensile strength.
3. Welding
Welding functions as the primary method that manufacturers use to connect stainless steel components through the three techniques of TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, and resistance welding. TIG welding produces clean welds, which yield high-quality results that lead to minimal distortion of 304 stainless steel thin sheets. MIG welding enables manufacturers to produce products at faster rates, which results in reduced production expenses, but the resulting welded joints appear less visually desirable. Thin sheets can be joined through resistance welding, which operates at high speed by using spot and seam welding techniques.
4. Surface Finishing
Polishing and surface treatments improve both the appearance and the functional capabilities of stainless steel sheets. The main finishes of the product consist of No. 4 brushed finish, which creates an attractive satin surface, and mirror finish (No. 8), which produces a highly reflective surface. The finishes can be achieved through efficient processes, which depend on abrasive belts together with automated polishing machines. The surface passivation process uses acid solutions to remove surface contaminants while enhancing corrosion resistance, which enables materials to maintain their durability throughout prolonged periods.
5. Forming and Deep Drawing
The manufacturing process begins with stainless steel sheets, which enter molds or dies to create stamped or deep-drawn parts. Deep drawing process brings success when manufacturing products like sinks and bowls, and specialized industrial components. 304 stainless steel exhibits excellent ductility that enables it to endure extensive deformation without breaking, which makes it suitable for this application. Hydroforming and advanced forming methods enable designers to create complex shapes using the original material structure.
6. Annealing
The annealing process requires 304 stainless steel to be heated until it reaches approximately 1900°F (1038°C) and then undergo controlled cooling. The process results in material properties that combine reduced hardness with increased ductility while achieving internal tension relief throughout the material. The material requires this process because it enables operators to work with the product during subsequent bending and machining operations.
The combined strength of stainless steel, with its corrosion resistance, enables manufacturers to create precise and durable products through multiple fabrication techniques, which find applications in construction and medical device development, and food processing industries.
Benefits of 2B Finish
The 2B finish is one of the most flexible stainless steel finishes because it delivers identical visual results and operational capabilities across various use cases. The process begins with cold rolling, followed by heat treatment, which leads to the pickling stage, before the final step of skin rolling with light treatment. The procedure creates a surface that reflects light through its dull finish, which enables easy cleaning and maintenance for spaces that need both hygienic standards and lasting materials.
The 2B finish creates smoother surfaces, which decrease roughness to a Ra value range between 0.3 and 0.6µm because smoother surfaces provide better protection against corrosion, according to recent industry data. This material serves as the perfect solution for medical equipment production and food processing equipment manufacturing, and kitchen surface applications. The studies demonstrate that stainless steel with a 2B finish can resist harsh cleaning products and corrosive chemicals, which extends the material’s durability in extreme conditions.
The 2B finish provides an efficient surface for later processes, especially polishing and coating applications, because its smooth texture needs only light work before processing starts. Manufacturers prefer this finish because it costs less while delivering performance that matches their needs when compared to expensive finishes like mirror-polished or brushed surfaces. The material has gained industry-wide acceptance because it demonstrates dependable performance across multiple usage scenarios.
Challenges in Fabricating Stainless Steel Products
The process of making stainless steel products faces multiple difficulties, which arise from the material properties and the processing requirements. The material becomes harder to machine and shape because its strength and hardness properties create difficulties that exceed those found in metals with lower strength. The operation results in more tool damage problems, which require special equipment and methods to solve these problems, but they decrease production efficiency through higher expenses.
The process of controlling heat output during welding and cutting operations represents another major problem. Stainless steel develops a heat-affected zone (HAZ), which makes it lose its corrosion resistance when it experiences excessive heating. Manufacturers need to implement exact temperature management and thermal treatment procedures, which demand considerable time and financial resources.
The process of preserving stainless steel’s visual appearance and operational capabilities requires effective surface finish management together with contamination prevention measures. The material develops surface defects because it is vulnerable to damage from both scratching and contact with carbon steel equipment. Clean environments without any contamination represent the essential requirement for production because this requirement creates extra difficulties for operations.
The worldwide stainless steel market reached a value of approximately $112 billion during 2022, according to recent industry research, and it will experience a 5.6% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) between the years 2023 and 2030. The research and development activities in new technology fields require better machining processes, improved welding systems, and more durable tool materials to enhance production methods. The industries of construction, automotive, and aerospace will achieve cost-effective solutions through their successful management of these challenges.
Industry Applications of Stainless Steel Sheet
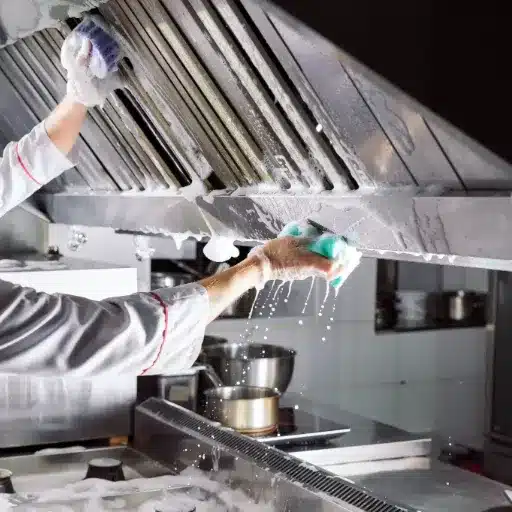

Food Processing and Hygiene Standards
The food processing industry needs stainless steel sheets because these sheets provide both exceptional strength and complete protection against rusting, together with their ability to maintain hygiene standards. Food production facilities depend on steel grades 304 and 316 because these materials provide excellent defense against acids and alkalis, and chloride materials, which need to remain sterile during operations.
The global food and beverage industry will raise its use of stainless steel from 2023 to 2030 because of the increasing demand for sanitary equipment used in food processing, which will result in a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 6.5%, according to current industry reports. The food processing industry uses stainless steel to build machinery, storage tanks, and conveyor systems, which need clean surfaces to stop bacterial growth and maintain food safety. The material surface prevents particle entry, which leads to effective cleaning and sanitizing processes that safeguard against potential contamination.
The U. S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) require that all equipment that directly contacts food products must use food-grade materials like stainless steel. The solution becomes attractive to sustainable manufacturing organizations because it combines recyclability with extended product life and cost-efficient operational expenses. Stainless steel remains the main material choice for food processing companies around the world because it achieves both functional requirements and environmental objectives.
Construction and Architectural Uses
The construction and architectural sectors depend on stainless steel because it provides strong, durable, and corrosion-resistant properties. The material serves as an ideal building material because its properties enable it to withstand harsh weather conditions, which makes it suitable for building facades and roofing systems, and structural supports. The latest research shows that the stainless steel market for construction purposes will grow at a rate of 5.3% annually from 2023 to 2030 because these materials become increasingly common in sustainable modern infrastructure projects.
Architectural designers use stainless steel in their creations because it provides a contemporary and streamlined aesthetic. The Petronas Towers in Malaysia and the Walt Disney Concert Hall in Los Angeles use stainless steel as their exterior material, which demonstrates both its visual beauty and practical benefits. The construction industry uses stainless steel for bridges, railings, and elevators, and decorative panels because these products can be recycled and require minimal upkeep, which helps achieve sustainability objectives.
Architects and engineers use advanced fabrication methods such as laser cutting and 3D printing to create complex and precise stainless steel designs, which modern manufacturing processes make possible. The increasing demand for environmentally sustainable buildings and green building materials strengthens the role of stainless steel as an essential material for developing city environments.
Automotive and Aerospace Industries
The automotive and aerospace industries use stainless steel because it delivers outstanding performance through its capability to withstand corrosion, its strength, and its ability to endure extreme temperature conditions. The automotive industry relies on stainless steel to produce exhaust systems, fuel tanks, and structural components. The global automotive stainless steel market reached a valuation of about $21 billion in 2022, according to recent industry data, and it is expected to expand at a 5.5 percent compound annual growth rate from 2023 until 2030 because the industry demands lighter materials for improved fuel efficiency.
The aerospace industry requires stainless steel to produce essential components, which include jet engine parts, landing gears, and fuselage cladding. The material proves ideal for space and aviation technology because it possesses high tensile strength together with outstanding thermal protection capacity. Stainless steel alloy developments enable aircraft designers to achieve weight reductions that improve performance while decreasing fuel consumption. The rising demand for next-generation aircraft, together with space exploration programs, establishes stainless steel as an essential material that will define future transportation systems.
Reference Sources
-
Application and Feasibility Analysis of Knowledge-Based Stainless Steel
This article discusses the properties of stainless steel, including its corrosion resistance, high strength, and excellent fatigue resistance, which make it suitable for various applications.
Read more on ScienceDirect -
The Feasibility of 316L Stainless Steel Mechanically
This research report focuses on 316L stainless steel, a widely used alloy in industrial applications, and evaluates its mechanical properties and feasibility.
Access the report here -
“Determination of spring-back of stainless steel sheet metal in ‘V’ bending dies”
- Key Findings: This research investigates the spring-back behavior of stainless steel sheet metal during “V” bending processes. It identifies factors influencing spring-back and provides recommendations for minimizing it.
- Methodology: The study uses experimental methods to test various stainless steel samples under controlled conditions, analyzing the results to determine the impact of material properties on spring-back.
Read more on ScienceDirect
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the characteristics of 304 stainless steel sheet as a material?
The 304 stainless steel sheet stands as the most versatile stainless steel material that people use in various applications. The material consists of iron, chromium, and nickel, which provide it with outstanding protection against both corrosion and oxidation. The material shows three main properties, which include its resistance to wear, its ability to be formed into various shapes, and its maintenance of strength under extreme heat. The product features a shiny, polished surface that serves both practical and decorative purposes.
Why is 304 stainless steel sheet commonly used in sheet metal applications?
The sheet metal industry uses 304 stainless steel sheet because it combines strong mechanical properties with effective protection against corrosion. The material functions effectively in industries that encounter regular contact with water and chemical substances and experience temperature changes. The material serves as a preferred choice for construction, automotive, and industrial applications because it can be easily transformed into different shapes.
How does 304 stainless steel compare to other stainless steel alloys?
The cost performance of 304 stainless steel remains better than all other stainless steel alloys because it provides optimal value for its manufacturing costs. The material provides excellent protection against corrosion; however, its performance in environments with high acid content or chloride exposure remains inferior to that of 316 stainless steel. The protection and strength of 304 stainless steel make it suitable for most applications, which leads to its common use as a material in various projects.
What are the typical applications of 304 stainless steel sheet?
The 304 stainless steel sheet finds usage in diverse industrial applications throughout multiple sectors. The material serves various purposes in kitchen equipment through its use in sinks and cookware, and in architectural elements through cladding and railings, and in medical, aerospace, and automotive applications. The product serves essential functions in environments that demand enduring sanitary products because of its ability to withstand damage and its versatile design.
Can 304 stainless steel sheet be used in high-temperature environments?
The 304 stainless steel sheet exhibits good performance in high-temperature conditions. The material maintains its structural integrity and oxidation resistance at temperatures reaching approximately 1,500°F (815°C). This makes it suitable for applications such as heat exchangers, industrial ovens, and furnace components. However, for prolonged exposure to higher temperatures, other specialized alloys may be more suitable.
Is a 304 stainless steel sheet easy to maintain?
The maintenance of 304 stainless steel sheet remains simple because its surface stays protected from rust, while its smooth finish enables easy cleaning. Regular cleaning with mild soap and water is often sufficient to maintain its appearance and functionality. People create surface damage by using strong cleaning products and rough cleaning tools. The product becomes popular in residential spaces and industrial settings because its maintenance requirements are minimal.