The manufacturing process for stainless steel components has been transformed through precision forging, which delivers exceptional strength and reliability to global industries. The advanced process not only improves the structural strength of stainless steel but also enhances its performance characteristics during use in demanding conditions, from aerospace engineering to heavy machinery. The article will demonstrate how precision forging accomplishes exceptional results while examining its effects on product durability, operational efficiency, and design possibilities. The detailed analysis of precision forging explains its essential role in modern stainless steel production processes, which benefits both industry professionals and regular people.
Introduction to Precision Forging

Definition and Overview of Precision Forging
Precision forging functions as a manufacturing process that creates metal components with exact specifications through a method that produces limited material waste. The precision forging technique creates products with dimensions that require no further machining work because they achieve near-net shape measurements. The technique finds common use in aerospace, automotive and biomedical industries because it produces components that demonstrate both superior mechanical performance and intricate design capabilities.
The precision forging market has experienced constant growth since recent data has shown that worldwide demand for lightweight high-performance parts continues to rise. The automotive industry relies on precision forging to produce components such as gears and connecting rods, and turbine blades, which require both exceptional strength and dependable performance. Precision forging establishes a production method that enables factories to achieve 65% more material efficiency than existing techniques, thereby generating substantial reductions in both production waste and manufacturing costs.
The main advantage of precision forging exists in its capacity to improve material characteristics through precision-controlled grain structure development. The process enables manufacturers to create materials that demonstrate uniform mechanical strength and toughness and fatigue resistance through its precise pressure and temperature control system. The current advancements in computer-aided design systems and simulation technology enable precision forging processes to achieve improved efficiency and precision and tailored production capabilities.
The new forging method creates environmentally friendly manufacturing through its ability to decrease waste and energy usage while enabling manufacturers to develop complex, high-quality parts that fulfill modern industrial requirements.
Importance of Precision in Forging Stainless Steel
Precision forging operates as a crucial production process that creates parts that need to withstand high stress while maintaining their strength and durability, and operational performance across different sectors. The global stainless steel forging market will experience substantial growth because various industries, including automotive and aerospace, and energy sectors, demand more stainless steel products. MarketWatch reports that the stainless steel forging market will achieve a $9.8 billion valuation by 2030 with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030.
The growth of precision forging is driven by its capability to create components that produce minimal material waste during manufacturing processes. Advanced forging techniques enable manufacturers to achieve 95% material utilization, which results in substantial decreases of scrap material when compared to traditional manufacturing methods. The manufacturing process results in cost savings for manufacturers while decreasing environmental damage.
Precision forging allows manufacturers to create intricate, detailed parts that deliver outstanding mechanical capabilities. The process enhances grain flow, leading to improved strength and toughness in stainless steel components. The aerospace industry depends on this capability because turbine blades and structural parts must perform at exceptional levels under high-stress conditions.
The implementation of CAD simulation and real-time monitoring technology enables manufacturers to achieve better process efficiency in precision forging operations. The technological advancements enable manufacturers to achieve tighter production tolerances, which result in faster manufacturing processes and better quality control procedures that enable stainless steel products to meet modern industrial requirements.
Key Terminology and Concepts
- Precision Forging Benefits
The use of precision forging enables two advantages because it improves material use and creates superior mechanical properties while decreasing the need for machining. Research conducted in various industries demonstrates that businesses can achieve 90 percent material efficiency with precision forging, which results in reduced waste when compared to traditional methods. The process increases component strength, which leads to better performance and longer lifespan, especially in aerospace and automotive, and energy industries that need dependable equipment. - Advanced Technologies in Precision Forging
Modern precision forging systems use advanced technologies, which include computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation software and automated process controls to create more effective processes. The current simulation methods now provide accurate results for material movement and temperature patterns, which help to attain better production results. The 2023 case study demonstrated that simulation-based forging methods cut development time by 30% while maintaining dimensional precision at the micrometer level. - Market Insights and Trends
The global precision forging market is projected to grow significantly with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2023 to 2030, according to data from a recent market analysis report. The automotive and aerospace industries require lightweight components, which drive this market demand. The precision forging industry will implement green forging innovations that focus on energy efficiency and carbon emissions reduction to create its future operations. - Real-Time Monitoring and Quality Assurance
Real-time monitoring technology plays an integral role in ensuring the quality of forged components. The sensors that manufacturers install in forging machines monitor three essential production parameters, which include temperature, pressure, and force. Reports indicate that manufacturers utilizing real-time monitoring systems have seen a 20% reduction in defect rates, which resulted in both cost savings and better product reliability.
These technological advancements, together with their data-based findings, demonstrate how essential precision forging functions in contemporary manufacturing processes. Manufacturers achieve successful competition in international markets by using sustainable practices together with modern technology.
Fundamentals of Stainless Steel Forging

Overview of Stainless Steel Grades
Stainless steel consists of different grades, which possess distinct characteristics that serve particular industrial needs. The primary grade classifications consist of austenitic stainless steels, ferritic stainless steels, martensitic stainless steels, duplex stainless steels, and precipitation-hardening stainless steels. The most common austenitic stainless steel grades include 304 and 316 because these alloys provide excellent protection against corrosion and convenient processing capabilities, and long-lasting performance. The added molybdenum content in grade 316 increases its resistance against pitting while enabling it to perform better in marine environments and areas exposed to chloride compounds.
Recent industry data shows that the global production of austenitic stainless steel exceeds 70 percent of total stainless steel output. Ferritic stainless steels which include grades 409 and 430, provide superior protection against stress corrosion cracking, and manufacturers use these materials in automotive exhaust systems and household appliances. The martensitic grades 410 and 420 exhibit high hardness characteristics, which make them suitable for manufacturing surgical instruments, knives, and valves.
Duplex stainless steels, which combine austenitic and ferritic structures, deliver both strong mechanical properties and protection against corrosion, making them suitable for use in oil and gas platforms and desalination plants, and structural components. The aerospace, chemical processing, and military sectors depend on 17-4 PH precipitation-hardening stainless steel to provide them with exceptional strength properties.
The development of stainless steel technologies has advanced through ongoing research into better alloy compositions and more efficient production techniques, which have resulted in improved operational efficiency, environmental sustainability and better industrial performance.
Characteristics of 304 Stainless Steel
The austenitic stainless steel alloy 304 shows exceptional effectiveness as a commonly applied material. The material provides outstanding protection against corrosion, together with high strength and excellent formability, because its main composition consists of iron, chromium and nickel. The composition of 304 stainless steel includes 18-20 percent chromium and 8-10.5 percent nickel, which enables the material to withstand oxidation and corrosion across multiple environments, which includes mildly acidic conditions.
The essential characteristics of 304 stainless steel include:
- Corrosion Resistance: The material demonstrates outstanding protection against corrosion during its use in various environments that involve contact with water, acids, and wet chemicals, making it suitable for both food-grade and medical-grade applications.
- Mechanical Properties: The material 304 steel demonstrates a combination of strength and flexibility, which results in a yield strength of 215 MPa 31 183 psi and an ultimate tensile strength of 505 MPa 73 236 psi.
- Thermal and Temperature Performance: 304 stainless steel maintains its performance capability up to 870°C 1600°F for intermittent usage and 925°C 1700°F for continuous operation. The material enables use in high-temperature settings that require equipment like heat exchangers and ovens.
- Formability and Fabrication: The metal can undergo roll-forming and stamping, and welding processes without losing its strength. The process of cold working 304 steel results in increased hardness and strength of the material.
- Surface Finish: The material reaches a highly polished state, which produces an attractive appearance that simplifies cleaning, making it perfect for use in architectural designs, kitchen spaces, and medical devices.
The current 304 stainless steel processing techniques have achieved environmental sustainability advancements through waste production reduction and better material consumption management. The material shows multiple applications for different industries, which include construction and automotive, food processing, and chemical manufacturing operations.
Comparison of Steel Alloys Used in Forging
The evaluation of steel alloys used in forging requires assessment of four key factors, which include mechanical strength, corrosion resistance and workability, and cost-effectiveness. The material 304 stainless steel stands out as a commonly used alloy because it provides exceptional protection against corrosion through its high chromium and nickel content. The material finds its application in sectors that require protection against both moisture and chemical exposure, such as marine and food processing and medical environments.
The 316 stainless steel alloy provides enhanced corrosion protection through its additional molybdenum content, which makes it a preferred choice for environments that demand chemical processing and coastal infrastructure protection against chloride and salt air exposure. According to industry research the corrosion resistance of 316 steel increases by 20 percent when exposed to chloride-rich environments compared to 304 stainless steel.
AISI 1045 carbon steel has become the preferred material because it offers high strength combined with low cost. Carbon steels provide excellent machinability while their tensile strength ranges from 570 MPa to 700 MPa, which makes them suitable for use in automotive parts, heavy equipment and tools. Proper coating and maintenance are essential for carbon steels because their unprotected state leads to rusting, which restricts their applications in areas with high humidity and chemical exposure.
Manufacturers have achieved higher material performance since current alloying and heat treatment methods produce energy-efficient results during their forging operations. The research results demonstrate that businesses can achieve more sustainable production practices when they use optimized forging parameters, which decrease material waste by 15%.
Alloy selection requires specific application knowledge because the selection process depends on three essential parameters, which include operating temperature and environmental exposure, and mechanical stress.
Advantages of Precision Forging for Stainless Steel Components
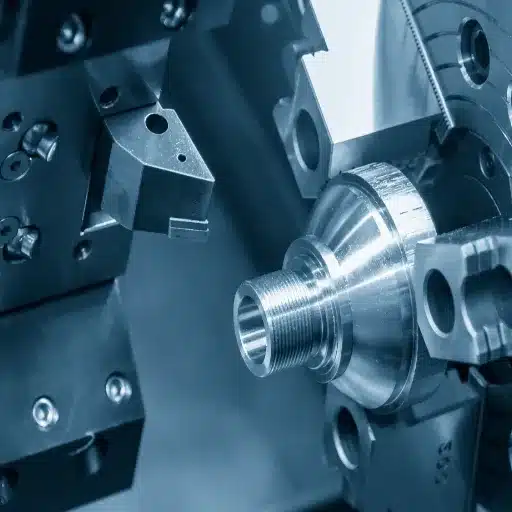
Improved Corrosion Resistance through Precision Forging Process
The precision forging method for stainless steel component production delivers exceptional corrosion resistance, which enhances product lifespan and operational performance in various environmental conditions. The process creates a microstructure, which achieves material refinement through metal grain alignment, to decrease both porosity and crack pathways and all types of defects. The research shows that components of stainless steel made through precision forging display 20 percent improved resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion when compared to parts made through traditional machining and casting methods.
The marine and chemical processing and medical fields prefer high-performance grades that include 316L stainless steel because this material can endure harsh operating conditions without experiencing major degradation. The latest developments in forging technologies use computer-aided simulations to achieve maximum material flow and uniformity, which results in decreased corrosion vulnerability for the forged products.
The application of contemporary techniques enables manufacturers to achieve two goals because they improve product performance and product lifespan while decreasing production costs through reduced material waste and better energy efficiency, which represents progress toward sustainable industrial practices.
Better Mechanical Properties of Forged Products
The industrial sector uses forging processes because these methods enhance the material’s mechanical properties during high-stress usage. The recent study demonstrated that forged components experience substantial improvements to their tensile strength and their ability to withstand fatigue and impacts. The research demonstrates that forged steel crankshafts deliver 30 percent better fatigue strength compared to cast steel crankshafts, which makes them suitable for use in both the automotive and heavy machinery sectors. The directional strength of components that experience cyclic loading improves through fiber alignment, which results from the forging process.
Industry reports show that forging creates mechanical benefits because it reduces porosity while achieving a uniform grain structure. The closed-die forging process produces parts that achieve 20 to 50 percent stronger performance compared to machined parts made from bar stock. The aerospace and defense, and energy industries require essential components that need to function under extreme conditions, and forging serves as the best method to produce these components. The manufacturing advancements showcase how essential forging remains for contemporary production methods, which establish it as a major element that boosts product performance and product reliability.
Forged Stainless Steels Provide Superior Strength and Durability
The strength and toughness of forged stainless steel materials surpass those of stainless steels that other manufacturing methods produce. The recent research shows that forged stainless steels display 30 percent better fatigue strength than components that manufacturers produced through casting and machining. The forging process produces an aligned grain structure, which boosts both tensile strength and impact strength of the material.
Forged components demonstrate superior resistance against wear and corrosion and thermal fatigue, which makes them suitable for use in extreme operating conditions. Forged 316 stainless steel proves itself as an exceptional choice for energy applications because it maintains peak performance after extended contact with corrosive materials like saltwater and acidic solutions. 17-4 PH stainless steel aerospace-grade forgings provide exceptional toughness, which enables them to handle severe temperature changes without losing their structural integrity.
The strong features of these materials extend the operational life of components while decreasing their replacement and maintenance requirements, which results in reduced overall costs throughout their operational life. The latest developments in forged stainless steels explain their widespread use in industries that prioritize safety and durability and operational efficiency.
Processes and Technologies in Precision Forging
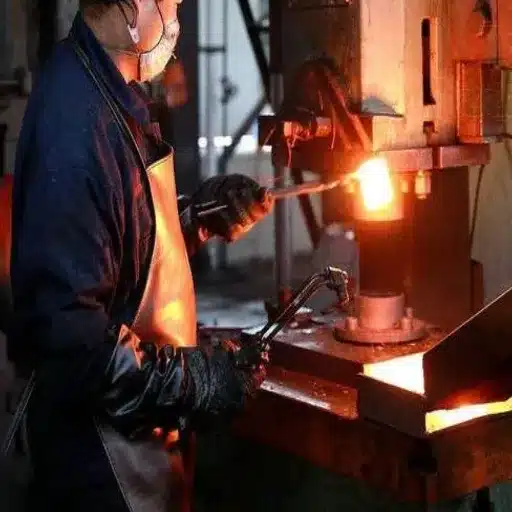

Die Forging vs. Open Die Forging Techniques
The metal shaping process has two primary techniques, which use die forging and open die forging to serve specific industrial applications and different manufacturing requirements.
Die Forging uses custom-made dies to create products that meet exact specifications and deliver consistent manufacturing outcomes. The method delivers exceptional results in mass production because it meets the requirements of the automotive, aerospace, and medical fields, which need to produce identical products with complex designs. The current research findings show that the die forging method creates lower material waste because its process achieves material utilization of 95% or higher than conventional machining techniques. The modern die forging technology progress has established significant production time reductions because current equipment can process 500 parts each hour.
Open Die Forging provides better operational capabilities through its ability to process large and heavy items. The process creates metal components through the application of pressure between two dies, which have either flat surfaces or shaped designs to create different metal products, including shafts, sleeves, and rings and large steel components. Open die forging provides significant advantages to energy production and shipbuilding industries, which require specially designed large components. Research indicates that open-die-forged parts demonstrate better mechanical properties because their ductility and toughness enable them to handle directional grain flow, which occurs during the forging process.
The two methods use advanced technologies like computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) to boost their operational accuracy and work productivity. Simulation software enables predictive modeling because it allows designers to test their ideas without conducting physical tests which results in decreased spending. The forging industry undergoes a technological transformation through these technologies, which create environmentally friendly and efficient production methods.
The Role of Heat Treatment in Forging
Heat treatment plays a critical role in the forging process because it improves the mechanical properties, durability, and performance of forged components. The metallurgical process requires materials like steel or other alloys to undergo heating and holding, and cooling until they reach their target properties, which include enhanced strength, hardness, and toughness.
Recent research found that organizations have developed a new heat treatment method that combines controlled cooling cycles with heat treatment to boost steel components’ fatigue resistance by 30%. Industry reports show that 70 to 80 percent of forged products undergo heat treatment, which enables them to meet the strict quality standards that aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery industries require.
The industry has adopted induction heating as the main technique for selective heat treatment because it enables operators to control temperatures while achieving 50 percent energy savings compared to conventional furnace systems. Automation and real-time monitoring systems support these methods, which lead to better operational efficiency and lower error rates while producing high-quality forged products.
The global forging industry has recognized the importance of evolving heat treatment technologies, with market reports indicating an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5% in heat treatment services by 2028. The innovations demonstrate how essential heat treatment procedures are to upcoming forging processes, which use established methods with contemporary technological progress.
Innovations in Forging Technology and Equipment
The industrial sector has benefited from forging technology advancements that deliver improved operational efficiency, together with better accuracy and reduced environmental impact. The adoption of robots and automated systems in forging processes represents the most important advancement in this sector. Automated forging systems create various benefits, which include faster production times, consistent outputs, and less material waste. The global forging market, which had a valuation of about USD 83 billion in 2022, will experience growth at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.9% between 2023 and 2030 because of rising automated technology adoption.
The introduction of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technology into forging operations transforms existing predictive maintenance and quality control systems. AI systems evaluate extensive production data to determine when machines will break down, which enables companies to plan maintenance activities that lead to reduced operational expenses. The trend represents a part of the manufacturing world that is currently transforming itself through digital technologies under the Industry 4.0 framework.
The development centers on advanced materials and 3D printing technology, which has emerged as a key factor. The innovations enable the development of intricate, high-performance forged components that satisfy the strict requirements of aerospace, automotive, and defense industries. The strength-to-weight ratio and durability of forged titanium alloys make them an increasingly common choice for aircraft production.
The forging industry continues to move away from traditional practices toward environmentally sustainable methods. The industrial sector has increased its usage of technologies that prioritize energy efficiency through induction heating and the implementation of environmentally safe lubricants. These programs work to decrease the carbon emissions produced by forging facilities to support international sustainability objectives.
The advancement of these technologies creates a future in which forging operations will achieve higher efficiency and accuracy while establishing better, environmentally sustainable practices that meet the changing needs of various global industries.
Real-World Applications of Precision Forging

Industries Benefiting from Stainless Steel Forgings
The industrial demand for stainless steel forgings exists because this material offers strong performance, together with its ability to resist corrosion and its multiple application options. The following list presents essential industries that depend on precision-forged stainless steel components for their vital operations.
- Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry uses precision-forged stainless steel components to create jet engines, airframes, brackets, and landing gear. The aerospace forging market will experience a 6.3% CAGR growth between 2023 and 2030, according to current market research, because the aviation industry needs lightweight, durable materials. - Automotive Industry
The automotive industry uses stainless steel forgings to manufacture crankshafts, gears, connecting rods, and various other components. These components protect against high-stress situations while maintaining operational efficiency. Recent reports show that precision forging has become more popular for electric vehicle components because the EV market will reach more than $980 billion by 2028. - Oil and Gas Industry
Pipelines and drilling operations use stainless steel forgings to create valves, flanges, and fittings because this material can endure both corrosive substances and high-pressure environments. The sector’s focus on operational safety and efficiency continues to boost demand for forged stainless steel products. - Construction and Architecture
Architectural structures and heavy equipment frequently incorporate stainless steel forgings for their durability and aesthetic appeal. Reports show that stainless steel demand in the construction industry is expected to see a steady increase, especially in regions focusing on infrastructure development, such as the Asia-Pacific. - Medical Industry
Medical professionals use stainless steel forgings to produce surgical instruments and orthopedic implants, and medical machinery because these materials demonstrate biocompatibility and maintain their integrity during sterilization. The global medical device market, which heavily depends on forged components, will reach $800 billion by 2030 according to research estimates.
The examples demonstrate how stainless steel forgings serve diverse industrial applications while creating economic value for multiple sectors. Their role in innovation and sustainability ensures their relevance in continuously evolving global markets.
Case Studies of Successful Forging Applications
- Aerospace Industry
The aerospace sector depends on stainless steel forgings because these materials deliver superior strength, together with their lightweight design and capacity to withstand extreme conditions. The creation of aircraft landing gear and engine components, and airframe structural parts relies on forged materials as essential elements. The global aerospace forging market is expected to expand at a 7.2% compound annual growth rate between 2023 and 2030 because of rising air travel needs and improvements in aircraft production methods, according to recent market research. - Automotive Industry
The automotive industry uses forgings to produce essential components, which include crankshafts and gears, and connecting rods. The durability and high-performance capabilities of forged parts make them indispensable for the efficiency and safety of vehicles. The global automotive forging market reached over 41 billion dollars in 2022, according to reports, and experts predict that it will continue to grow as electric vehicle production increases. The automotive industry needs forgings that can adapt to its current challenges, according to this expansion. - Renewable Energy Sector
The renewable energy industry is increasingly adopting stainless steel forgings for components used in wind turbines, hydroelectric stations, and solar panel frameworks. The forged parts serve outdoor applications because their resistance to corrosion, combined with their extended lifespan, protects against damage. The wind energy forging market will exceed $7 billion by 2028 because sustainable energy needs and global carbon neutrality efforts will drive market growth, according to a study. - Construction and Infrastructure
The construction industry relies on stainless steel forgings for vital components that shape bridges and skyscrapers, and other structures that require strong structural support. Their strength enables them to endure both pressure and environmental challenges, which results in an extended lifespan and protective measures. The construction industry requires high-quality forged materials to execute substantial projects, which will begin after global construction revenue reaches $15 trillion by 2030.
The case studies show that stainless steel forgings create important industrial advantages by delivering strength and dependable performance, which supports sustainable operations while fostering both technological advancement and economic development.
Examples of Forged Products and Their Uses
- Automotive Components
The automotive sector requires forged materials, which manufacturers use to produce vital automotive parts such as crankshafts, gears, and axle beams. The forged components deliver vehicle safety and durability because they possess outstanding strength, which enables them to endure severe stress situations. The global automotive forging market reached a value of about $41 billion in 2022, according to current market data, and it will expand at a compound annual growth rate of 4.5% between 2023 and 2030 because of increasing demand for lightweight, durable automotive parts. - Aerospace Applications
The aerospace industry uses forged components to produce essential parts, which include turbine disks and engine cases, and landing gears. The manufacturing process of these parts requires precision because they need to survive extreme environmental conditions, which include intense heat and pressure. The research shows that the aerospace forging market will experience substantial growth because new forging technologies enable the production of lightweight materials, which include titanium and aluminum, that improve fuel efficiency and performance. - Industrial Machinery
Industrial machinery production depends on forge manufacturing, which creates components that operate under extreme weight and stress conditions. The global industrial machinery forging market shows continuous growth while manufacturers focus on developing energy-efficient production methods and using eco-friendly materials. - Oil and Gas Industry
Stainless steel forgings function as essential components for oil and gas operations because they provide valves and flanges, and fittings that endure harsh, abrasive conditions. The market size for forged products in the oil and gas sector is expected to grow because exploration and production activities are rising across the world.
The forging industry achieves market requirements through modern technology and data-driven manufacturing methods while propelling sustainable development and innovative solutions. The forging industry uses contemporary technology together with data-based production processes to meet market demands while driving sustainable growth and inventive developments.
Reference Sources
-
The effects of hot forging on the preform additive-manufactured 316 stainless steel parts – Examines the combination of hot forging and heat treatment on additive-manufactured 316L stainless steel parts.
-
Microstructure and mechanical behavior of 316L liquid phase sintered stainless steel with boron addition – This study investigates the role of boron in the processing of AISI 316L stainless steel and its effects on structural integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is precision forging, and how does it benefit stainless steel structural integrity?
The precision forging method generates precise parts through its advanced forging methods, which produce exact measurements and superior surface characteristics while using little raw material. The method establishes total elimination of internal empty spaces in stainless steel materials which also delivers uniform microstructural development throughout the material to produce components with enhanced strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance. The process delivers precise outcomes that eliminate the necessity of conducting extensive material treatments after the initial processing step. The process maintains all material elements intact. The process maintains all material elements intact. The process maintains all material elements intact. The process maintains all material elements intact.
How does precision forging contribute to sustainability in manufacturing?
Precision forging proves to be an environmentally friendly manufacturing technique because it generates less material waste and requires less energy than standard forging processes. The precision forging process requires advanced technology and data-based manufacturing systems to achieve maximum material efficiency for each created product. The process achieves high efficiency, which leads to smaller carbon emissions during manufacturing operations. This outcome supports the current industry trend toward implementing sustainable production methods.
Why is precision forging important in the oil and gas industry?
The oil and gas industry requires components that can endure extreme environmental conditions, including high-pressure situations, high-temperature situations, and corrosive environments. The production of stainless steel valves and flanges, and fittings requires precision forging as an essential manufacturing process. The method guarantees that these components will achieve optimal structural performance, which delivers the increased strength necessary for safe operations in the industry.
What role does modern technology play in precision forging?
The process of precision forging depends on modern technology because it enables manufacturers to use data for decision-making while achieving better accuracy throughout the entire production process. Advanced computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation tools optimize component design while minimizing defects. The real-time monitoring systems of forging processes guarantee both product consistency and specification compliance, which result in products that possess superior quality and dependability. The real-time monitoring systems of forging processes guarantee both product consistency and specification compliance, which result in products that possess superior quality and dependability.
Can precision forging reduce costs in manufacturing?
The process of precision forging leads to major cost reductions through its ability to decrease material waste and its capacity to cut down on both machining and post-processing work. The high accuracy and uniformity of forged components eliminate the expense of correcting defects or imperfections. This advantage results in more cost-effective production cycles which maintain both product quality and product structural integrity of stainless steel components.
What makes forged stainless steel superior to other manufacturing methods?
The properties of forged stainless steel surpass the characteristics of products that undergo casting. The forging process eliminates internal defects and aligns the grain structure to the shape of the part. This process strengthens the material while increasing its fatigue resistance. The process of precision forging improves surface quality and dimensional precision, which enables equipment to function at peak efficiency in extreme conditions that exist throughout the oil and gas industry.






