Cutting stainless steel might scare the faint-hearted as such, but with the right tools and technique, this job can be performed by both the skilled and the unskilled. From large industrial projects to a sort of intricate piece for home improvement, understanding the different methods for cutting stainless steel is crucial for how you achieve precision and efficiency. Thus this guide will cover the best ways to cut stainless steel, the tools best suited, and some practical tips for getting an excellent finish. Whether you are a tradesperson or a hobbyist working with stainless steel, this article will help to demystify the process and assist you in choosing which way suits your needs.
Understanding Stainless Steel and Its Challenges
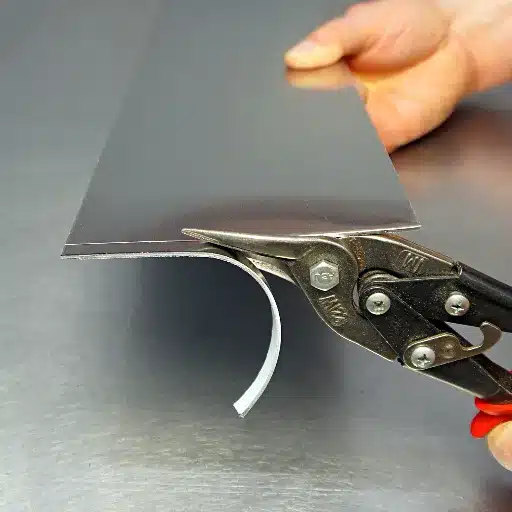
A great deal of force runs through the making of stainless steel, and the cutting of such a finely tempered steel requires immense skill. I’ve noticed that knowing these aspects is important to picking the right advice for a particular job.
Significance of Cutting Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is characteristically strong and corrosion-resistant and hence preferred in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and automotive. Yet it is probably one of the toughest materials to cut due to its hardness. The importance of cutting stainless steel cannot be understated because improper and inefficient methods may waste material and give away the quality of the end product, and if all that is not enough, increased cost of production.
Industry Insight:
Clean and accurate cutting is necessary to maintain the structural integrity and intangibility qualities required by stainless steel components. For example, in the aerospace industry, the performance of equipment and its safety can be affected by accurately cut stainless steel parts. Recent trends show an expected annual growth rate of 6.3%, serving as a source of concern for the cutting industry needing to produce at high speed with minimum waste and ease of workflow.
Common Cutting Problems
Stainless steel is a way up high in the list of challenging materials to produce because it offers several difficulties to the fabricator aiming at high precision and efficiency:
Hardness of the Material and Heat Resistance
Because of its high strength and heat resistance, stainless steel is difficult to cut as compared to softer metals, such as aluminum. The hardness of the material, however, promotes wear of the cutting tools and requires the use of strong and special blades or cutting tools; the heat produced in the cutting procedure can also distort the material itself if uncontrolled. Recent research shows that employing high-speed cutting tools equipped with cooling systems could result in a reduction of up to 30% in thermal deformation.
Tool Wear and Maintenance
Because of the toughness of stainless steel, tools might lose their sharpness quite quickly, especially in conventional methods of cutting. For instance, in mechanical cutting, and more specifically, bandsawing, blades will have to be sharpened or replaced very often to ensure precision throughout; water jet and laser cutting, on the other hand, although actually being good and efficient methods, require also a lot of maintenance on their nozzles or laser generators to keep good performance as time goes on.
Essential Tools and Equipment for Cutting Stainless Steel
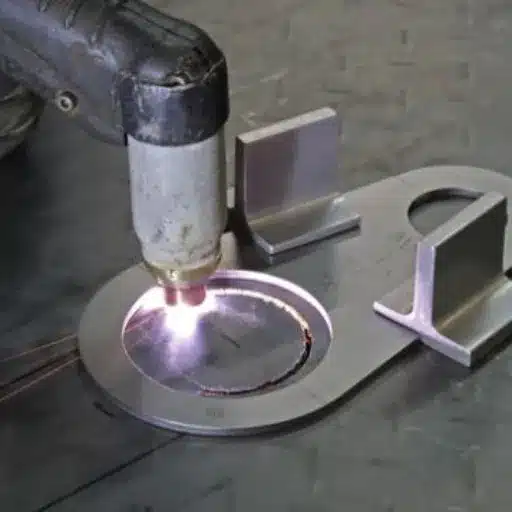

Stainless steel cutting requires making sure that one has the right tools and equipment such as the plasma cutter, an angle grinder, or a laser cutting machine. Depending on the precision and finish required, one should also have a workspace sufficient to ensure safety and efficiency.
Angle Grinder: Versatility and Speed
The angle grinder probably represents the most versatile tool in making stainless steel cuts, offering a combination of precision, speed, and easy handling. With the right cutting disc, this tool can perform a wide range of cutting operations, from small and precise cuts to heavy industrial applications. Grinding discs of abrasive nature, such as aluminum oxide or zirconia, are applied with the angle grinder for cutting through very tough materials like stainless steel.
Choosing the correct grinder diameter along with the respective disc is essential for good performance. The most commonly used discs measure either 4.5 or 7 inches in diameter, with the former being more suited to detail work and the latter being able to make shorter bulk cuts faster. When employed well, an angle grinder can cut the stainless steel sheets or bars very quickly, usually in minutes, maintaining excellent consistency.
Performance Data:
According to some new trade insights, depending on various factors, such as the thickness and variety of stainless steel, an operator makes full use of cutting discs and can attain material removal rates as high as 3.5 cubic inches per minute. Good cutting technique should mean that the material is secured properly and placed on stable footing to allow for a steady, ergonomic stance during cutting; this includes wearing gloves and goggles for protection to ensure the best efficiency, safety, and accident prevention.
Circular Saw and Its Applications
One of the most versatile and widely used power tools in present construction and woodworking, a circular saw with a toothed or abrasive disc blade is made to efficiently and accurately cut wood, metal, plastic, or masonry. What separates this saw from other saws is its ability to make straight, clean cuts either along the grain (rip cuts) or across the grain (crosscuts). Hence it is needed throughout framing to cabinetry.
According to recent market reports, the power tools market—including circular saws—is expected to touch $43 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of nearly 4.5%. Such growth depicts a high need for quality-performing tools for residential and commercial uses. The modern circular saw is manufactured mainly in two configurations: corded and cordless. Cordless ones, powered by lithium-ion batteries, offer greater mobility and are quite favored by DIY amateurs and contractors in isolated areas.
Safety Precautions When Cutting Stainless Steel
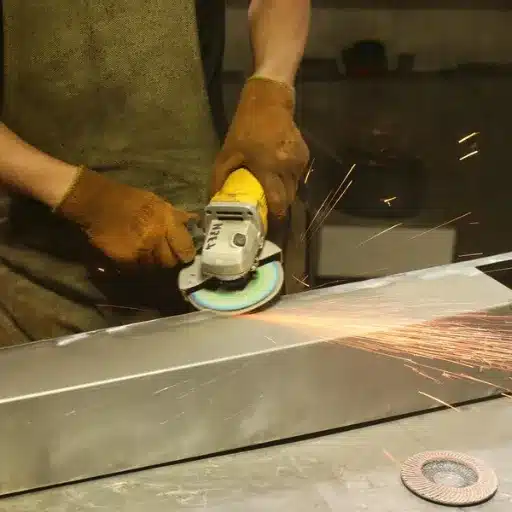

When cutting stainless steel, it is advisable to wear safety goggles, gloves, and a dust mask because of the flying debris or fine metal particles. Use a blade designed for metal and place the material on a cut-off stand or vice to prevent its movement. Also, keep the whole work area well-ventilated and follow a steady hand to ensure that all cuts are precise and safe.
Protective Gear and Equipment
Working with rotary tools or cutting stainless steel requires appropriate protective gear and equipment, which are essential in protecting the operator and reducing risks. Industry safety guidelines specify that the following items are necessary for protection:
Safety Glasses or Goggles
If the eye gets attacked in cutting materials such as stainless steel, sparks, metal shards, or debris could cause serious damage. Therefore, this is the utmost importance for safety glasses worthy of ANSI Z87.1 certification with high resistance to impacts. Approximately 60% of the cases of eye injury in the construction industry are due to the lack of or incorrect use of protective eyewears.
Cut-Resistant Gloves
Hands are often exposed to sharp edges or metal fragments during cutting. With some financing, cut-resistant gloves rated EN 388 would provide an effective barrier against lacerations.
Hearing Protection
Heavy noise over a long period caused by tools like circular or rotary saws can lead to permanent hearing disability. Noise-canceling earmuffs or earplugs with a Noise Reduction Rating (NRR) of 25 dB or higher are recommended. Studies show that rotary saws and tools generally exceed noise levels of 85 dB, which is considered hazardous for hearing.
Best Practices for a Safe Working Environment
The creation of a safe working environment plays a central role in preventing work-related injuries and observing a culture of safety and productivity. Effective safety practices, based on the most recent data and recommendations, provide for the protection of employees and the maintenance of workspaces that are productive.
Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
It entails addressing and eliminating potential hazards as the first step to ensuring safety in the workplace. A recent safety report reveals that organizations practicing regular risk assessments have 25-30% fewer workplace-related injuries than those that do not. Risk assessments help point out areas that warrant immediate attention or improvements, whether it has to do with faulty machinery, slipping hazards, or improper ergonomics.
Employee Training and Awareness
Teaching employees about tools and equipment and the proper way to work and practices that pertain to a safe operation lowers the chance of accidents, according to studies. In 2023, it was found that companies that had continuous safety education saw a 45% reduction in injuries. Training programs need to also include proper procedures for emergencies, lifting, and locating hazards.
Appropriate Safety Gear
Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as helmets, gloves, and steel-toe boots must be easily accessible and mandatory in high-risk environments. Studies show that wells that enforce PPE compliance saw up to a 37% reduction in injury claims. PPE should be certified to recognize standards such as ANSI/ISEA for maximum protection.
Step-by-Step Methods to Cut Stainless Steel
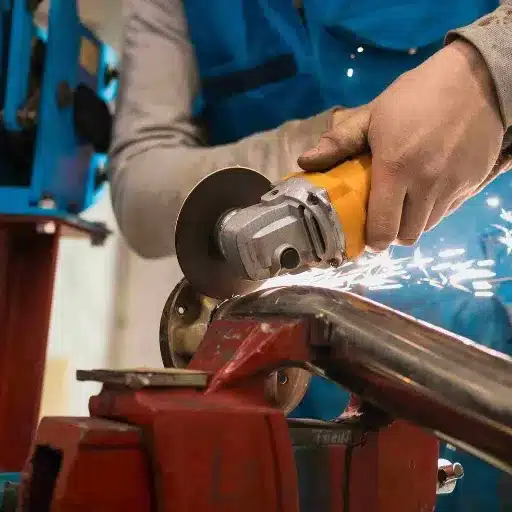

To cut stainless steel, I would follow these steps: First, pick the tool most suitable for the job: a hacksaw, an angle grinder, or a plasma cutter depending on the thickness and the precision required. Then, mark the cutting line with a marker or a scribe for reference. Next, put on safety gear like gloves and goggles and clamp the steel firmly to prevent movement. Finally, carry out the cut making steady pressure and take your time to allow for a clean finish.
Using the Angle Grinder
One of the best used tools for stainless steel cutting is an angle grinder when used with precision. Follow these steps to cut stainless steel using an angle grinder:
- Choose the Right Disc: Always go for a good-quality cutting disc appropriate for stainless steel. The aluminum oxide or ceramic abrasive discs are excellent choices, as they have good durability with scant heat damage. Thin discs with thickness varying between 1.0–1.6mm are great for steel as they provide precision.
- Wear Protective Gear: Put on your PPE: safety goggles, hearing protection, gloves, and a dust mask. When cutting stainless steel, sparks and small debris are generated, so without personal protection, accidents could happen.
- Secure the Material: Make sure that the stainless steel is placed on a solid working surface and clamped tightly to prevent any movement during cutting. This guarantees that the person cutting will maintain control and keep it accurate, as well as reduce the risks involved.
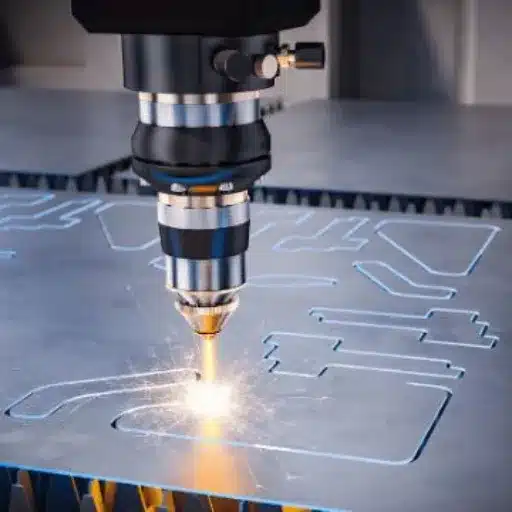
Laser Cutting Methods
Laser cutting is a highly efficient and precise method popularly used in manufacturing industries to cut materials such as metals, plastics, and composites. As opposed to traditional cutting methods, laser cutting employs a focused beam of light to melt, burn, or vaporize the material. This allows for intricate patterns with smooth edges and minimum copious wastage.
Performance Metrics:
When considering cutting speed, depending on the thickness and type of material, a modern laser cutting machine can achieve speeds of 60 inches per second(ips). These machines are often coupled with automation systems, which in turn, increase productivity by 20%-30% in high-volume production environments. Altering the laser power settings is key, with increased power density used for thicker materials, thus clean and efficient cuts are ensured.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
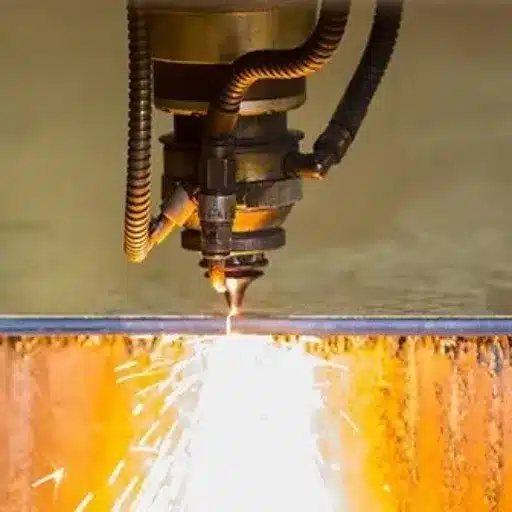

One of my troubleshooting steps revolves around the laser settings; thus, I first look at power, speed, and focus. If the cuts are not clean indeed, I look at the lenses and mirrors to check for dirt or damage and verify their alignment. I also check if the material in use corresponds to the parameters set; otherwise, inconsistencies will cause problems.
Solving Problems of Overheating and Warping
The stainless steel is subject to overheating and warping mainly because of high friction and prolonged heat generation. Moreover, these plants hinder good quality of cut and can eventually damage the cutting tools and the workpiece itself. So, to lessen heat buildup, you ought to use blades meant for stainless steel cutting. Bi-metal or carbide-tipped blades are highly recommended since they provide greater resistance to heat, offer durability, and increase protection against excess wear.
Besides, applying cutting lubricant will intensify heat dissipation and reduce friction between the blade and the stainless steel during cutting. Research shows that with the use of the right lubricant, cutting temperatures can lower by as much as 40%, allowing blade integrity to stay intact along with a polished surface. Additionally, the jigsaw should be operated at lower speed settings so that heat will not be concentrated too quickly around the cutting area.
Inaccurate Cuts
Inaccurate cutting must be solved because the stainless steel key ensuring high-quality components and reducing waste; various reasons lead to inaccurate cutting, ranging from improper tool setup, human error, and inaccurate calibration of equipment. Research shows that the use of advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) that has tolerances as low as ±0.001 inch can reduce the chance of inaccuracies. Moreover, CNC plasma cutting systems, when maintained properly, offer not only precision cutting but also optimize material usage by reducing kerf width and assuring repeatable accuracy.
Furthermore, there must be the use of modern cutting software solutions such as CAD/CAM integration. Industry reports have placed software-driven precision as capable of improving the error margin by up to 40%. Right material alignment on the cutting table is equally important. Studies have disclosed that misalignment leads to dimensional inaccuracies of over 0.02 inches, thus compromising product quality. Operators must factor in regular calibration within the interval when operating machines; it is recommended every 100 hours of operation to maintain cutting precision.
Reference Sources
-
KDM Fabrication
Stainless Steel Cutting 101: A Practical Guide
This source offers a comprehensive guide on various methods for cutting stainless steel, including hacksaws, power tools, and precision techniques. It is a practical resource for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. -
Tuofa CNC Machining
12 Ways to Cut Stainless Steel | Metal Cutting Guide
This blog provides an in-depth look at different tools and methods for cutting stainless steel, tailored to varying thicknesses and applications. It is particularly useful for understanding the tools required for specific tasks. -
TOPS Precision
How To Cut Stainless Steel: 12 Best Ways
This article discusses multiple cutting methods, such as laser cutting, plasma cutting, and abrasive saws, highlighting their benefits and applications. It is a reliable source for professionals seeking precision techniques.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I cut stainless steel sheet metal?
Depending on whether the stainless steel sheet metal is thin or thick, you can use metal shears or a circular saw fitted with a suitable blade for cutting metal. For straight cuts, a band saw and a jig saw with an appropriate blade are also very useful. The blade must be appropriate, else it may spoil the material and leave a poor cut.
What are 10 ways to cut stainless steel?
There are multiple techniques to efficiently cut stainless steel. Here are the ten:
- Angle grinder with a cutting wheel
- Band saw
- Metal shears
- Circular saw with a metal cutting blade
- Jigsaw with a metal blade
- Plasma cutter
- Laser cutting machine
- Rotary tool with a cutting attachment
- Hacksaw
- Water jet cutting
Each method varies in precision and is suited for different thicknesses of stainless steel.
Can stainless steel be cut without damaging it?
Yes, stainless steel can be cut without damaging it if the tools and the technique are right. For instance, use blades or wheels that are made especially for cutting metal, and hold steady to have clean, straight cuts. The use of lubricants, which prevent overheating due to friction during the cutting operation, would also contribute towards preventing damage.
What is the right blade for cutting stainless steel rods?
A high-speed steel (HSS) blade or carbides tipped blade with metal cutting intent will be an ideal choice for cutting stainless steel rods. These types of blades are meant for thicker stainless steel and know how to handle the heat generated during the cutting process. Keep the blades sharp to ensure efficient, proper work.
How do I ensure a clean cut when cutting stainless steel?
Ensure a clean cut while cutting stainless steel by having the right blade or cutting tool used by maintaining a steady feed rate. Never force the tool through the material for it creates a jagged edge. Lubricants can also reduce friction and heat while aiding in smoother cuts. Try cutting a few scraps first to see how it feels.
What methods are used to cut thick stainless steel?
When you are cutting thick stainless steel, it is good to use the method that will lessen heat and stress on the material. The thicker materials suit well for plasma cutting and laser cutting. The band saw and angle grinder with a metal cutting wheel can also serve in manual methods. The speed and pressure must be altered according to the thickness of the steel you want to cut.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of cutting stainless steel requires the right combination of tools, techniques, and safety measures. Whether you’re using an angle grinder for quick cuts or laser cutting for precision work, understanding the material’s properties and choosing the appropriate method will ensure successful results. Remember to prioritize safety, use proper protective equipment, and take your time to achieve clean, accurate cuts that maintain the integrity of your stainless steel projects.








