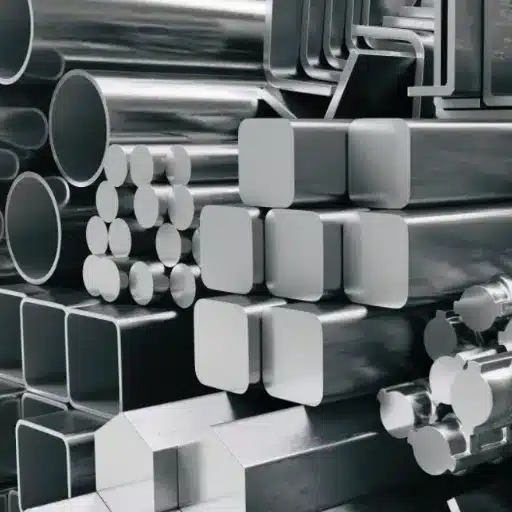
The selection of materials used in industrial projects, construction work, and manufacturing operations determines both operational efficiency and material strength across time. The 316 stainless steel sheet serves as the best choice because it provides excellent corrosion resistance and delivers strong material performance across different applications. The guide delivers important information to engineers who need advanced materials, to contractors who require trustworthy systems, and to business owners who want to understand procurement procedures. The presentation will explain the essential features of 316 stainless steel while demonstrating its various industrial applications and delivering critical guidance for selecting the best products. The material demonstrates its suitability as a primary option used by many industries because it provides multiple industry applications.
Introduction to 316 Stainless Steel Sheet

What is 316 Stainless Steel?
The material shows industrial use because alloy 316 stainless steel can endure severe environmental conditions without suffering rust. The material functions as an austenitic stainless steel, which belongs to the 300-series family because its main components consist of iron, chromium and nickel with molybdenum included as a supplemental element to boost corrosion resistance against chlorides and acidic environments.
The standard makeup of 316 stainless steel contains 16 to 18 percent chromium and 10 to 14 percent nickel, and 2 to 3 percent molybdenum, together with small amounts of carbon, manganese, silicon, and iron. The substance develops exceptional defense properties, which protect against pitting and crevice corrosion, making it appropriate for use in marine environments and chemical processing and locations exposed to saltwater and severe chemical contact.
316 stainless steel exhibits distinct mechanical characteristics that distinguish it from other materials. The material reaches a tensile strength of 579 MPa, which equals 84,000 psi, and it has a yield strength of 290 MPa, which equals 42,000 psi. The material maintains its excellent toughness attributes throughout all cryogenic temperature ranges, which enables its use in multiple operational fields.
The essential property of 316 stainless steel enables it to withstand high heat conditions up to 1600–1700°F (870–925°C) without losing its strength. The material shows stability, which allows it to function in heat exchangers and power generation systems and multiple industrial operations that require high-temperature resistance.
316 stainless steel is popular in construction, food processing and medical devices, and aerospace industries because it combines strength and corrosion resistance with durability. The non-reactive surface of the material makes it the ideal choice for industrial equipment that needs to maintain sanitary standards, which makes it suitable for pharmaceutical and food production industries.
Differences Between 316 and 316L Stainless Steel
The primary difference between 316 stainless steel and 316L stainless steel exists because their carbon content determines their appropriate applications. 316 stainless steel contains a maximum carbon content of 0.08%, whereas 316L operates as a low-carbon grade with 0.03% maximum carbon content. 316L contains less carbon, which enables it to resist carbide precipitation during welding, thus preserving its corrosion protection within welded areas.
The two materials demonstrate different abilities to withstand environments that cause corrosion. The two grades deliver strong protection against corrosion. 316L provides superior protection against intergranular corrosion, which occurs after the welding process. 316L emerges as the better metalworking solution for projects that require extreme environmental conditions.
The mechanical properties of 316 stainless steel and 316L stainless steel display slight differences. 316 stainless steel achieves metal strength through tensile strength and yield strength that exceeds the metal strength of 316L. The tensile strength of 316 metal reaches 515 MPa, while 316L has a tensile strength of 485 MPa. The strength difference between these materials has little effect on how they perform in most real-world situations.
316L stainless steel serves various applications because its composition enables its use in welding environments where localized corrosion must be prevented. 316L stainless steel finds application in marine environments, chemical processing, and medical implants. 316 stainless steel finds application in situations that demand increased hardness and strength, but welding operations do not need to be controlled.
The two grades maintain their popularity in industrial sectors. The selection process between the two grades requires evaluation of project needs, together with operational costs and existing environmental conditions. The right grade selection guarantees that equipment and structures will operate at their best while maintaining durability and trustworthiness throughout their use in challenging environments.
Overview of Stainless Steel Sheets and Plates
The superior strength and anti-corrosive properties of stainless steel sheets and plates make them vital to various industrial applications because these materials possess multiple operational functions. The flat-rolled steel products manufacturer utilizes different stainless steel grades for their production process, which uses 304 and 316 grades as the primary grading system to create particular features that satisfy distinct industrial requirements.
The thickness of sheets begins at 0.5mm and reaches approximately 6mm, whereas plates start at 6mm and continue to grow thicker. Stainless steel sheets serve as the preferred material for both automotive manufacturing and kitchen equipment production and decorative element creation because these sheets combine lightweight characteristics with adaptive functionality. The construction sector, together with heavy machinery production and industrial activities, uses stainless steel plates because these materials deliver essential strength and long-lasting performance.
The global stainless steel market has shown continuous expansion because the construction sector, automotive industry, and healthcare field demand increasing quantities of stainless steel materials. According to market research, the stainless steel market reached a value of approximately USD 133 billion in 2022 and the market will grow at an annual rate of 5% until 2030.
Modern cold rolling and hot rolling manufacturing methods, which function at current technological standards, create high-quality sheets and plates that show top-grade surface textures and precise size specifications. The products enable customers to select from various finishing choices, which include brushed and polished, and matte finishes, based on their visual and operational requirements.
The new stainless steel technologies, which create improved performance results, lead to sustainable development because stainless steel can undergo complete recycling. The industries that develop sustainable solutions choose sheets and plates because these materials deliver exceptional quality while protecting the environment.
Key Properties and Benefits of 316 Stainless Steel Sheet

Corrosion Resistance
The primary characteristic of 316 stainless steel demonstrates its outstanding ability to withstand corrosion, which enables its usage in harsh environmental conditions. The material develops its ability to resist pitting and crevice corrosion through its high molybdenum content, which typically ranges between 2 and 3 percent of its total weight. The latest research shows that 316 stainless steel maintains its structural integrity at chloride concentrations up to 1000 ppm, whereas 304 stainless steel shows significant degradation under those same testing conditions. The material shows its high resistance against both acidic and alkaline conditions, which include sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid and salt spray. The properties of 316 stainless steel make it the most suitable choice for marine applications, medical equipment, and food processing facilities because these environments experience continuous contact with corrosive substances.
The material achieves extended operational life because its corrosion protection mechanism decreases the need for maintenance work and equipment replacement expenses during its operational period. The industries that need reliable performance during difficult conditions should choose 316 stainless steel sheets because they provide outstanding strength and environmental protection.
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of 316 stainless steel sheets make them an ideal material for industrial applications and marine environments. The properties of these materials ensure they will remain functional and intact when faced with extreme operational challenges. The following section presents essential details about the material’s mechanical properties:
- Ultimate Tensile Strength: The material can endure heavy loads without failure. The tensile strength of the material ranges from 515 to 720 MPa, which equals 75 to 105 ksi.
- Yield Strength: The material exhibits a yield strength of 205 MPa, which corresponds to 30 ksi and indicates the stress level at which it starts to permanently bend.
- Elongation at Break: The material shows a 40% elongation at break, which indicates its ability to stretch without breaking when tested over a distance of 2 inches.
- Hardness: The material has a Rockwell B hardness rating of approximately 95, which protects it from wear and damage that occur through surface contact.
- Impact Resistance: The material demonstrates exceptional impact resistance because 316 stainless steel maintains operational capabilities at temperatures below the freezing point, which allows its use in cryogenic environments.
The mechanical properties of 316 stainless steel remain intact at high temperatures because the material melts between 1371 and 1399°C, which equals 2500 to 2550°F. The system operates efficiently at continuous temperatures reaching 925°C. For intermittent use, the system operates effectively up to 870°C. These characteristics enable the material to perform effectively in environments with both high pressure and high temperature conditions.
The material 316 stainless steel becomes a dependable industrial material because it combines high tensile strength with ductility and toughness, which remain intact during extreme environmental conditions.
Heat Resistance and Annealing Process
The stainless steel 316 material shows outstanding ability to withstand heat, which makes it perfect for use in high-temperature settings. The material maintains its structural strength and oxidation protection until 1600°F (870°C) for continuous use and until 1650°F (899°C) for temporary usage. The material achieves its heat resistance through its elevated chromium and nickel levels, which protect against oxidation during extended heating periods.
The mechanical and physical characteristics of 316 stainless steel reach their optimal state through the essential annealing process. The standard annealing process requires heating the material between 1900°F and 2150°F (1040°C and 1177°C) before conducting rapid cooling through water quenching. The heat treatment process removes internal stresses that developed during production while it enhances the grain structure and returns ductility and toughness to the steel for safe operation in extreme work environments.
The material demonstrates thermal conductivity of 13.4 W/m·K at 500°F (260°C), which shows its ability to dissipate heat in high-temperature conditions. The 316 stainless steel material demonstrates better mechanical properties and corrosion resistance through annealing, which benefits industries such as chemical processing, aerospace, and marine construction. The proper annealing process reduces carbide precipitation risks, which endanger corrosion protection under specific environmental conditions.
Comparison with Other Types of Stainless Steel

316 vs. 304 Stainless Steel
Industrial applications extensively involve the 316 and 304 stainless steel grades because these metals exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance, together with their strong mechanical performance. The two materials exhibit different properties that define their suitable applications in industrial settings.
- Composition Differences
The 316 stainless steel composition contains 2-3% molybdenum, which enables the metal to resist chloride-based marine corrosion. 304 stainless steel lacks molybdenum, which creates protective functions that enable the material to resist pitting and crevice corrosion attacks in saltwater environments with chemical exposure. - Corrosion Resistance
The 316 alloy demonstrates superior protective capabilities against corrosion, which occurs in environments with saltwater and chemical exposure. In marine environments, 316 shows better protection against rusting and staining threats than 304. 304 alloy maintains its corrosion resistance but performs better in environments that include kitchen equipment and building materials. - Cost Comparison
The presence of molybdenum in 316 stainless steel raises production costs by 20-30% when compared to 304 stainless steel, which depends on current worldwide market prices. The 304 material presents cost benefits because it provides sufficient protection against corrosion for applications that do not require extensive corrosion defense. - Applications
The medical industry, chemical processing facilities, and marine construction projects use 316 because it offers exceptional protection against various operational conditions. The 304 material serves multiple purposes in food processing machines, kitchen appliances, and building designs that do not face severe environmental conditions. - Mechanical Properties
The two materials demonstrate comparable tensile strength, which measures at about 515 MPa, and yield strength, which reaches around 205 MPa, because they meet requirements for structural applications. The improved corrosion protection of 316 stainless steel results in longer operational durability when used in difficult working conditions. - Temperature Resistance
The high-temperature resistance of 316 stainless steel surpasses that of 304 stainless steel because it maintains both its structural strength and corrosion protection during exhaust system and furnace system functions. Users need to understand their work environment and specific application needs before choosing between these two commonly used stainless steel grades.
Performance of 316 Stainless Steel in Different Environments
The unique combination of chromium, nickel, and molybdenum in 316 stainless steel results in outstanding material characteristics that endure various environmental circumstances. The section that follows evaluates the performance based on specific conditions, which researchers verified through their application of current research findings.
- Marine Environments
The 316 stainless steel material shows enhanced protection from corrosion in marine environments, which exceeds the protective abilities of all standard stainless steel materials. The material’s molybdenum content provides enhanced protection against chloride-based corrosion, which includes both pitting and crevice corrosion. Research shows that 316 stainless steel maintains its structural integrity during lengthy exposure to high saltwater conditions, which makes it suitable for use in shipbuilding dock components and underwater pipelines. - High-Temperature Environments
The alloy shows excellent oxidation resistance at temperatures up to 1600°F 870°C. The study found that 316 stainless steel maintains its mechanical properties in environments with both high temperature and industrial heat exchangers or furnace components. The material provides better performance than 304 stainless steel at temperatures above 1500°F 815°C because it can resist both thermal fatigue and stress corrosion cracking. - Acidic and Chemical Processing Environments
The material can withstand acidic solutions, which contain sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and acetic acid, because of its molybdenum content. Research highlights that 316 stainless steel’s corrosion rate is significantly lower when tested in environments containing up to 5% sulfuric acid at room temperature. - Cryogenic Environments
The excellent toughness of 316 stainless steel at extremely low temperatures makes it an ideal material for cryogenic applications. The material maintains its strength and ductility properties until it reaches -320°F -195°C. The material’s properties make it suitable for use in storage tanks, cryogenic vessels, and piping systems that exist in industrial environments. - Food and Pharmaceutical Environments
The non-toxic and non-reactive nature of 316 stainless steel makes it a consistent choice in the production of food-grade containers, surgical instruments, and pharmaceutical equipment. The recent evaluations of the system show that it meets the strict hygiene and safety requirements established by FDA and ISO certifications, which guarantee the absence of metallic contamination.
The superior properties of 316 stainless steel create reliable performance in extreme conditions, which leads to reduced maintenance costs and extended equipment lifespan. The material demonstrates premium-grade status for critical industrial and commercial applications because of its capacity to withstand various marine high-temperature, chemical, cryogenic, and hygienic environments.
Cost Considerations: 316 vs. Other Alloys
The total cost assessment of 316 stainless steel requires two evaluations, which assess both its initial material costs and the total benefits of its extended performance, which different alloys provide. The market research shows that 316 stainless steel costs 20-30% more than 304 stainless steel because of its higher molybdenum content and better corrosion resistance. The current market prices show that 304 stainless steel sells for $2.50 to $3.00 per pound, while 316 stainless steel sells for $3.25 to $4.00 per pound.
The initial capital required for 316 stainless steel installation exceeds initial expenses, yet this material provides better financial value during product usage in conditions that involve high chloride levels, extreme temperature ranges, and strong chemical contact. The material provides extended operational life because 316 stainless steel resists pitting and stress corrosion cracking, together with wear, which decreases the need for maintenance activities.
Duplex stainless steels and titanium alloys provide customers with equivalent protection against corrosion, yet they charge customers 50-200% more than 316 stainless steel, which costs 316. The solution provides 316 as the ideal midpoint option, which delivers affordable solutions to businesses while enabling outstanding performance across multiple sectors, including marine operations, healthcare practices, and food processing activities. The process of choosing materials for critical projects requires professionals to comprehend the relationship between cost and performance throughout different project stages.
Common Applications of 316 Stainless Steel Sheet

Industrial Applications
Industries across multiple sectors utilize 316 stainless steel sheets because these sheets provide exceptional resistance to corrosion, and they maintain high strength, and their structural integrity remains intact throughout extended time periods. The chemical processing industry uses 316 stainless steel to build containers and piping systems and heat exchangers, which must withstand extreme chemical conditions that include both acidic and chloride-rich environments. The material provides protection against pitting and crevice corrosion, which makes it suitable for industries that work with seawater and brine solutions.
The most recent market information indicates that the worldwide stainless steel industry has maintained steady growth since 316 stainless steel obtained its significant market presence. The marine industry depends on 316 stainless steel because it offers essential materials for building ships, installing underwater pipelines, and constructing desalination plants. The data shows that marine-grade stainless steel 316 extends equipment and infrastructure lifespan by 40 when compared to traditional carbon steel materials.
The FDA has established 316 stainless steel sheets as suitable for high-purity and sterile environments that exist in pharmaceutical and food processing facilities because these sheets maintain their hygienic properties that protect against production contamination. The latest surface treatment and coating advancements work to enhance material performance through their capacity to fulfill precise industrial requirements.
Use in Marine Environments
The 316 stainless steel sheets deliver complete protection for marine environments because they display outstanding resistance against saltwater corrosion. The material achieves its strength to resist pitting and crevice corrosion through the addition of molybdenum, which protects against seawater chloride ion damage. Recent research shows that 316 stainless steel maintains its structural integrity when exposed to chloride levels up to 1000 ppm, which makes it an ideal choice for use in shipbuilding, offshore oil platforms, and underwater piping systems.
The use of 316 stainless steel in marine structures provides cost savings for maintenance because its long-lasting durability decreases the need for repairs throughout its extended operational period. Studies show that using 316 stainless steel components instead of less corrosion-resistant materials can extend infrastructure lifespan by up to 30%. The combination of these characteristics and its strong mechanical performance makes 316 stainless steel an essential material for environments with extreme saltwater exposure.
Applications in Food Processing and Pharmaceuticals
The food processing industry and the pharmaceutical industry depend on 316 stainless steel because it provides excellent corrosion protection and easy surface maintenance. The material functions as a non-reactive element that maintains the sanitary standards needed for food and pharmaceutical products in environments that require high hygiene levels.
The food processing industry uses 316 stainless steel components, which include mixers, tanks, and conveyor systems, to ensure food safety through their ability to stop contamination. The material maintains its structural integrity and operational capabilities throughout food production processes because it resists damage from acids, alkalis, and chlorides. Research shows 316 stainless steel offers double the protection against pitting and crevice corrosion in salty and acidic environments when compared to 304 stainless steel.
The pharmaceutical industry requires strict control of sterilization processes. The material 316 stainless steel serves multiple purposes, including cleanroom use, bioreactor operation, and surgical instrument manufacturing, because it can endure steam sterilization and chemical cleaning procedures. The 316 stainless steel vessels and equipment, which industrial data shows decrease maintenance expenses while satisfying strict international standards, including FDA and EU requirements.
The two sectors use this alloy extensively because it delivers high strength and dependable performance and maintains sanitary conditions to enhance productivity while protecting public health.
Factors to Consider When Purchasing 316 Stainless Steel Sheet

Choosing the Right Size and Thickness
When buyers select 316 stainless steel sheets, they need to choose both size and thickness because these attributes determine how the material performs in different use cases. Standard sheet thicknesses extend from 0.5 millimeters to 6 millimeters, while customers have the option to request custom dimensions that meet their particular needs. Projects that need lightweight materials with adaptable characteristics require architects to use thinner sheets, which building facades require, and automotive manufacturers need to produce car components. The industrial machinery and marine equipment require thicker sheets, which provide the essential strength and durability needed for their operational needs.
The project needs require the sheet size selection, which helps to decrease both material waste and project expenses. The demand for custom fabrication services has risen because these services provide businesses with precise sheet cutting capabilities, which enable them to reduce costs. The manufacturing databases show that customized sizing decreases scrap rates by 15%, which depends on the complexity of the specific project. The evaluation of these factors enables businesses to choose the most effective and economical stainless steel sheet that fulfills their operational requirements.
Understanding Different Finishes: Including 4 Finishes
The finish of stainless steel sheets serves as the most essential element, which determines both their visual appeal and their operational capabilities. The #4 finish serves as a standard choice for customers who want an alternative to its satin, brushed, and directional finishes. The steel surface achieves its smoothness through fine abrasive belts and pads, which create a consistent pattern across the entire material.
The #4 finish serves as the perfect solution for situations that require both visual appeal and practical use. The material finds extensive application in architectural designs, kitchen equipment, and automotive parts because its surface treatment effectively prevents fingerprint marks and minor scratches, which maintain a neat and professional appearance. The #4 finish remains the most common choice for commercial kitchen stainless steel because it provides hygienic benefits and simple cleaning, which industry studies show to be true.
The #4 finish provides protection against moderate levels of damage, which makes it appropriate for most operational environments. The Global Stainless Steel Market Outlook shows that demand for this finish increased by almost 8% during 2022 because the hospitality and construction industries raised their investment levels.
The #4 finish requires maintenance work to achieve its full advantages. The material maintains its original surface texture through non-abrasive cleaning operations, which also extend its lifespan. This finish combines functionality with a sleek aesthetic, making it one of the most versatile options available.
Finding a Reliable Stainless Steel Sheet Supplier
The process of selecting a trustworthy stainless steel sheet supplier requires consideration of multiple factors, which affect the supplier’s material quality, product availability, and price competitiveness. The global stainless steel market will experience growth from 2023 to 2030 at a 6.2% CAGR because construction, automotive, and consumer goods sectors require more stainless steel. The market growth has resulted in more supplier options, but businesses need to identify the most suitable vendor for their partnership needs.
- Quality Standards and Certifications
The supplier needs to show industry standard compliance through ISO 9001 certification, which requires them to implement quality management for all production activities. The American Society for Testing and Materials takes the ASTM certification system as a fundamental product testing standard, which assesses product reliability and performance standards. - Range of Products and Customization Options
The supplier needs to provide multiple stainless steel grades, which should include both #4 and #2B and mirror finishes. The project requirements will benefit from the suppliers who provide exact customization through their specific thickness and dimensions and pre-cut offerings. - Supply Chain and Inventory
Modern industries need their products to arrive at their facilities within the shortest time possible to maintain their market competitiveness. The supplier requirements should include suppliers who maintain strong supply chain operations, together with dependable inventory systems. Suppliers can achieve faster delivery times and reduced delivery costs through their access to local and regional warehouse facilities. - Customer Reviews and Industry Reputation
A trustworthy supplier will show customer reviews together with service testimonials from their previous clients. Established companies demonstrate high customer satisfaction, which results in strong customer retention and leads to trade publications recognizing their achievements. - Competitive Pricing and Additional Services
A supplier who charges fair prices, together with material testing and certification, and technical support services, will establish itself as a dependable business partner. Global Metal Suppliers received a top-three ranking among stainless steel distributors because they provide complete post-purchase support to their customers.
The right partner selection will provide both product excellence and dependable project results. The supplier comparison process requires you to examine their available products while testing samples and keeping communication channels open. The leading suppliers of your project requirements will deliver high-quality results that meet your needs.
Reference Sources
-
Stainless Steel Grade Chart – Stanford University
This document provides detailed information on the corrosion resistance and properties of 316 stainless steel. -
Technical Data – BLUE SHEET – Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory
This technical sheet provides data on the oxidation resistance and scaling rates of 316 stainless steel.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main characteristics of 316 stainless steel sheet metal?
The combination of 316 stainless steel sheet material to protect against both marine environments and chemical environments provides exceptional corrosion resistance. The material contains molybdenum, which improves its protection against both pitting and crevice corrosion damage. The material enables welding processes while it maintains high tensile strength and withstands elevated temperature conditions. The material provides industrial and architectural applications with one of the most flexible and durable solutions available.
Which stainless steel type shows better performance than 316 stainless steel?
The 316 grade stainless steel provides better protection against extreme environmental conditions than all other existing stainless steel grades. The 316 grade contains more molybdenum than 304 stainless steel, which other people consider a common grade. The material provides an ideal solution for operations that take place near saltwater and for environments that exist in chemical processing.
What are the common applications of 316 stainless steel sheet?
The exceptional qualities of 316 stainless steel sheet make it suitable for multiple industrial applications. The material is used in marine equipment, chemical processing plants, medical instruments, food preparation equipment, and architectural facades. The material fulfills both practical needs and visual needs through its capacity to maintain a polished look and its ability to resist corrosion.
What factors should you evaluate when you buy 316 stainless steel sheets?
The evaluation process for 316 stainless steel sheets requires assessment of thickness and dimensions, surface finish, and industry standard compliance. You must confirm that your supplier delivers material certification together with their quality assurance processes. The project’s success depends on selecting a dependable supplier who provides support after you make a purchase. The product development process requires you to maintain open communication with the team about your specifications.
Are there different finishes available for 316 stainless steel sheet?
The 316 stainless steel sheets provide multiple finish options, which enable them to fulfill particular project needs. The available finishes include a No. 2B dull matte finish and a No. 8 highly reflective mirror finish. Polished finishes serve aesthetic purposes, while practical and industrial needs require brushed and mill finishes. Your finish selection should depend on your intended application and maintenance requirements.
What makes 316 stainless steel suitable for high-temperature applications?
316 stainless steel maintains high performance during high temperatures because it possesses strong oxidation resistance and stable thermal properties. The material can endure constant heat of 1600°F, which corresponds to 870°C, while it tolerates brief exposure to temperatures reaching 1700°F, which equals 925°C. The material’s strong construction provides enduring performance, which makes it suitable for use in furnaces, heat exchangers, and various other high-temperature industrial processes.